
In Top-down design, parts’ shapes, sizes, and locations can be designed within the assembly. These parts do not change their shape and size based on your design unless you choose a different component. Bottom-up design is the preferre d technique for previously constructed, off-the-shelf parts, or standard components like hardware, pulleys, motors, etc. These changes are then seen in the assembly. To change the parts, you must edit them individually. You first design and model parts, then insert them into an assembly and position the parts. The Solidworks ™ knowledge base defines the two as follows:īottom-up design is the traditional method. Some systems, via associative copying of geometry between components, also allow a top-down method of design. This is called bottom-up design and is supported by nearly all CAD 3D systems. The various individual data files describe the 3D geometry of individual components and are assembled r through a number of sub-assembly level s before creating an assembly that describes the whole product. At this stage, it is critical that the design evolution be visible to all of the design engineers that are involved in the project.
#Assembly 4 cad free#
This free access during the design phase ensures that while working on their own parts, each designer can check to make sure that his/her part works within the overall design and functionality. New parts are added as they are created, with each design engineer having access to the assembly model while it is a work in progress. The head designer generally has access to all of the assembly models and is responsible for merging them together into the final machine design. Often, several different design engineers may be working concurrently on a machine or product that has multiple assembly parts. Each of these components with the complete assembly is represented as solid models.
#Assembly 4 cad software#
These types of sophisticated software systems are designed to handle multiple files that represent the individual components that make up an entire product or machine. Each component within an assembly is represented as surface models.Īssembly modeling in CAD refers to both the technology and the techniques used by 3D CAD through which the design intent of a part or assembly is accurately and unambiguously described by a 3D virtual model. What is Assembly Modeling?Īssembly modeling is a technology and process of using CAD (computer-aided design) and product visualization software to design components of a product.
In fact, entire college courses can be devoted to various projects that are designed to develop 3D design skills and knowledge.
#Assembly 4 cad how to#
Learning how to carry out complex operations within a 3D program in order to create a “working” assembly model can take time.
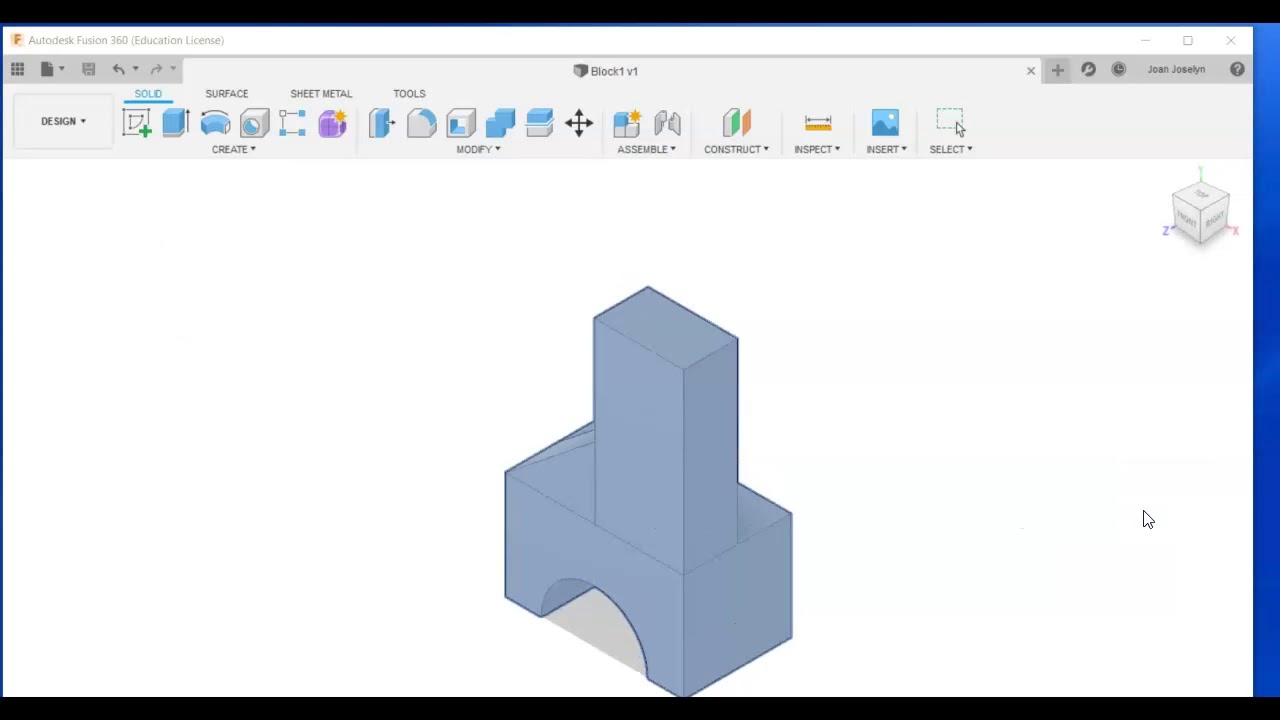
Using a 3D so ftware program, such as CATIA, various 3D parts can be combined into complete assembly models by rotating the parts, sliding them, exploring various ways to join them and employing other design concepts that are far beyond the geometric representations of the 2D CAD. Hu, D., Hu, Y., Li, C.: Mechanical Product Disassembly Sequence and Path Planning Based on Knowledge and Geometric Reasoning.Traditional 2D drafting is capable of showing the geometry of simple 3D parts, however solid models extend that ability by being able to merge complex assemblies of parts into a complete mechanism. Viganò, R., Gómez, O.G.: Automatic assembly sequence exploration without precedence definition. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology 69(1), 1359–1371 (2013) Liu, X., Liu, Y., Xu, B.: A converse method-based approach for assembly sequence planning with assembly tool. Advances in Engineering Software 48, 17–26 (2012) International Journal of Production Research 40(2), 255–273 (2002)Ĭiszak, O.: Computer aided determination of the assembly sequence of machine parts and sets. Huang, Y.M., Huang, C.T.: Disassembly matrix for disassembly processes of products.
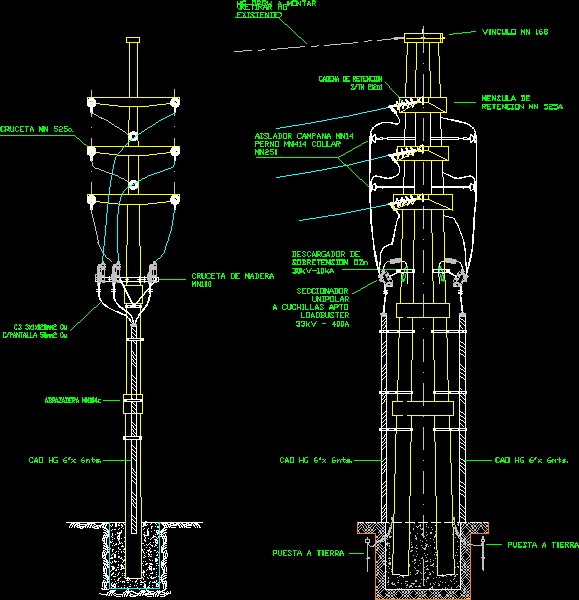
Dini, G., Santochi, M.: Automated sequencing and subassembly detection in assembly planning.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
